Luoyang Zhongtai Industrial Co., Ltd. |
|
Verified Suppliers
|
|
60kw Hydro Turbine Power Generation Equipment 20m Water Head 0.37m³/S Flow Rate
1.Basic introduction of hydraulic turbine
Hydraulic turbine is a power machine that converts the kinetic energy of water into mechanical energy, and is a hydraulic machine that uses water to do work. This product is an impact turbine of mixed flow type.
Hydraulic turbines are mostly installed in hydropower stations to drive generators to generate electricity. In a hydropower station, water from the upstream reservoir is led to the turbine through the diversion pipe, pushing the turbine wheel to rotate and driving the generator to generate electricity. The finished water is then discharged downstream through the tailwater pipe. The higher the head and the greater the flow, the greater the output power of the turbine.
2. Technical parameters of this product(Power Generation Equipment)
| Turbine parameters | Generator parameters | |||||||||
| Model | Water head (m) | Design under the head | Speed (r/min) | Model | Power (KW) | Voltage (V) | Current (A) | Speed (r/min) | Inlet valve (m) | |
| Flow rate (m³/s) | Power (KW) | |||||||||
| HL220-WJ-30 | 20 | 0.37 | 60 | 1000 | SFW50-6/368 | 50 | 400 | 90 | 1000 | 400 |
3. Overview of the impact turbine
Impact turbines can be divided into mixed-flow, axial-flow, inclined-flow and cross-flow types. In the mixed-flow turbine, the water flows radially into the water guide mechanism and axially out of the runner; in the axial-flow turbine, the water flows radially into the guide lobe and axially into and out of the runner; in the oblique-flow turbine, the water flows radially into the guide lobe and into the runner at an angle inclined to the main shaft, or flows into the guide lobe and the runner at an angle inclined to the main shaft; in the cross-flow turbine, the water flows axially into the guide lobe and the runner In cross-flow turbines, the water flows axially into the guide vane and the runner. Axial, cross-flow and inclined flow turbines can also be divided into fixed-paddle and rotating-paddle turbines according to their structure. In the fixed-paddle type the runner blades are fixed; in the rotating-paddle type the runner blades can be rotated around the blade axis during operation to accommodate changes in head and load.
All types of impact turbines are equipped with water inlet devices. The water inlet devices of large and medium-sized vertical shaft impact turbines are generally composed of a worm shell, fixed guide vanes and movable guide vanes. The function of the worm shell is to distribute the water flow evenly around the runner. When the head is below 40 metres, the worm shell of the turbine is often made of reinforced concrete cast on site; when the head is higher than 40 metres, the metal worm shell is often welded or cast as a whole. In impact turbines, the water flow fills the entire runner and all the blades are subject to the action of the water flow at the same time, so the runner diameter is smaller than that of impact turbines at the same water head. They also have a higher maximum efficiency than impact turbines, but the efficiency of the turbine is affected to varying degrees when the load varies. Impact turbines are equipped with tailpipes, whose function is: to recover the kinetic energy of the water flow at the outlet of the runner; to discharge the water flow downstream; and to convert this potential energy into pressure energy to be recovered when the installation position of the runner is higher than the water level downstream. For low head and high flow turbines, the kinetic energy at the outlet of the runner is relatively large, and the recovery performance of the tail pipe has a significant impact on the efficiency of the turbine.
4. Mixed-flow turbine characteristics
Francis turbine is one of the most widely used turbines in the world, invented by the American engineer Francis in 1849, so it is also called Francis turbine. Compared with the axial paddle type, its structure is simpler, its operation is more stable and its maximum efficiency is higher than that of the axial type, but when the head and load vary greatly, the average efficiency is lower than that of the axial paddle type, and the maximum efficiency of some of these turbines has exceeded 95%. Mixed-flow turbines are suitable for a wide range of heads, from 5 to 700 metres, but the most used are 40 to 300 metres.
The runner of mixed-flow type is generally made of mild steel or low-alloy steel castings, or with cast-welded structure. In order to improve the resistance to cavitation and sediment wear performance, can be in the easy cavitation parts welded stainless steel, or stainless steel blades, sometimes the entire runner can also be stainless steel. The use of cast-welded structure can reduce costs and make the runner size more accurate, the runner surface is smoother, which is conducive to improving the efficiency of the turbine, but also with different materials to manufacture the blade, the upper crown and the lower ring.
The runner of a Francis turbine looks more complex, with the water flowing horizontally from all around the turbine into the centre of the runner (radial inflow) and then turning to exit in a downward direction. The water entering the runner pushes the runner in the direction of the shaft core through the blades, and also pushes the runner in the downward direction through the blades. In other words, the water flow in the radial and axial direction through the blades are doing work. Therefore it is called a mixed-flow turbine, also known as an amplitude axial flow turbine.
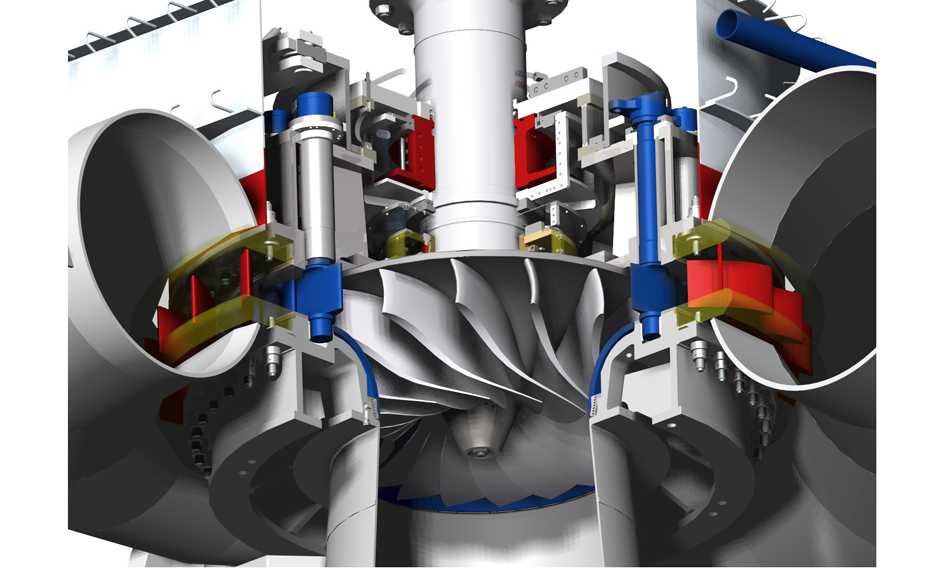
5. Power Generation Equipment photo explanation