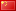
ZFeng 900 Series 630Kw-T-G General Vector Variable Frequency Drive
Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) is a power control device that
applies frequency conversion technology and microelectronics
technology to control AC motors by changing the frequency and
voltage of the motor's working power supply.
Working Principle
- Core components
Rectification: Convert alternating current into direct current.
Filtering: Smooth the DC voltage and reduce harmonic interference.
Inverter: Convert direct current into alternating current with
adjustable frequency and voltage.
Control unit: Implement algorithm control through a microprocessor
to adjust output frequency and voltage. - Speed regulation mechanism
V/f control: Maintain a constant voltage to frequency ratio to
ensure stable motor magnetic flux.
Vector control: Independently control torque and magnetic flux to
achieve high dynamic performance.
Direct torque control: Directly controlling torque and magnetic
flux, with faster response speed.
Protection Function
- Overcurrent protection: Monitor current to prevent overload.
- Overvoltage protection: Monitor voltage to prevent excessive
voltage.
- Undervoltage protection: Monitor voltage to prevent low voltage.
- Overload protection: Monitor the load to prevent motor overload.
- Grounding protection: prevent motor grounding faults.
- Short circuit protection: prevent output short circuit.
- Overfrequency protection: Limit the output frequency to prevent
overclocking operation.
- Stall protection: prevents the motor from stalling during
operation.
Selection And Usage Precautions
- Key selection points
Load characteristics: Select the appropriate frequency converter
based on the load type (constant torque, constant power, square
torque).
Power matching: The rated power of the frequency converter should
be greater than the rated power of the motor, with a margin left.
Environmental conditions: Consider factors such as temperature,
humidity, altitude, etc., and choose a frequency converter with
appropriate protection level. - Precautions for use
Installation environment: Avoid high temperature, humidity,
corrosive gases, and dust.
Grounding and shielding: Ensure good grounding and reduce
electromagnetic interference.
Maintenance: Regularly clean the heat sink, check cable connections
to prevent overheating and loosening.