Ucloud® Low noise Intelligent Dynamic air quality monitor PM2.5
detector for indoor air control
Automatic Dynamic Air detectors
Intelligent Air quality detector PM 2.5 indicator
Main Functions:
- Detection of indoor humidity and temperature
-
- Detection of carbon monoxide(CO) concentration
-
- Detection of volatile organic gases
-
- Detection of Customer-defined gas molecular data
-
- Send the detection data to the intelligent control panel
-
- Send detection data to the detection cloud platform
-
- Send the detection data to the dynamic sterilizer
Automatic Dynamic Air detectors
Intelligent Air quality detector PM 2.5 indicator
Low noise Intelligent Dynamic air quality monitor PM2.5 detector
for indoor air control
Technical Parameters
| Voltage | Power | N.W.(kgs) | G.W.(kgs) | Measure(mm) | Noise |
| AC100-240V | 2W | 0.4 | 0.6 | Φ135×40mm | 26Db |
| Suggest Using Environments: -10℃-50℃, RH<85% |
Automatic Dynamic Air detectors Intelligent Air quality detector PM
2.5 indicator
Low noise Intelligent Dynamic air quality monitor PM2.5 detector
for indoor air control
Detectable Items:
- 2.5 micron suspended particles(PM 22.5)
- Volatile organic matter
- Carbon dioxide
- Carbon monoxide
- Ammonia
- Hydrogen Sulfide
- Sulfur dioxide
- Oxygen
- Liquefied gas
- City gas
Automatic Dynamic Air detectors Intelligent Air quality detector PM
2.5 indicator
Automatic Dynamic Air detectors Intelligent Air quality detector PM
2.5 indicator
===============================================
Pollutants,
An air pollutant is a substance in the air that can have adverse
effects on humans and the ecosystem. The substance can be solid
particles, liquid droplets, or gases. A pollutant can be of natural
origin or man-made. Pollutants are classified as primary or
secondary. Primary pollutants are usually produced from a process,
such as ash from a volcanic eruption. Other examples include carbon monoxide gas from motor vehicle exhaust, or the sulfur dioxide released from factories. Secondary pollutants are not emitted
directly. Rather, they form in the air when primary pollutants
react or interact. Ground level ozone is a prominent example of a secondary pollutant. Some pollutants
may be both primary and secondary: they are both emitted directly
and formed from other primary pollutants.
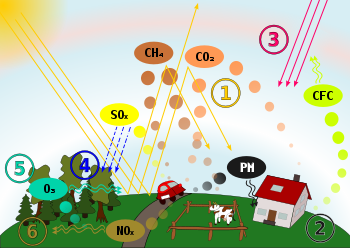
Schematic drawing, causes and effects of air pollution: (1)
greenhouse effect, (2) particulate contamination, (3) increased UV
radiation, (4) acid rain, (5) increased ground level ozone
concentration, (6) increased levels of nitrogen oxides.
Substances emitted into the atmosphere by human activity include:
- Carbon dioxide (CO2) - Because of its role as a greenhouse gas it has been described as "the leading pollutant"[5] and "the worst climate pollution".[6] Carbon dioxide is a natural component of the atmosphere, essential
for plant life and given off by the human respiratory system.[7] This question of terminology has practical effects, for example as
determining whether the U.S. Clean Air Act is deemed to regulate CO2 emissions.[8] CO2 currently forms about 405 parts per million (ppm) of earth's
atmosphere, compared to about 280 ppm in pre-industrial times,[9] and billions of metric tons of CO2 are emitted annually by burning of fossil fuels.[10] CO2 increase in earth's atmosphere has been accelerating.[11]
- Sulfur oxides (SOx) - particularly sulfur dioxide, a chemical compound with the
formula SO2. SO2 is produced by volcanoes and in various industrial processes. Coal
and petroleum often contain sulfur compounds, and their combustion
generates sulfur dioxide. Further oxidation of SO2, usually in the presence of a catalyst such as NO2, forms H2SO4, and thus acid rain.[2] This is one of the causes for concern over the environmental
impact of the use of these fuels as power sources.
- Nitrogen oxides (NOx) - Nitrogen oxides, particularly nitrogen dioxide, are expelled from high temperature combustion, and are also
produced during thunderstorms by electric discharge. They can be seen as a brown haze dome above or a plume downwind of cities. Nitrogen dioxide is a chemical compound with
the formula NO2. It is one of several nitrogen oxides. One of the most prominent
air pollutants, this reddish-brown toxic gas has a characteristic
sharp, biting odor.
- Carbon monoxide (CO) - CO is a colorless, odorless, toxic yet non-irritating gas.
It is a product of incomplete combustion of fuel such as natural gas, coal or wood. Vehicular exhaust is a
major source of carbon monoxide.
- Volatile organic compounds (VOC) - VOCs are a well-known outdoor air pollutant. They are
categorized as either methane (CH4) or non-methane (NMVOCs). Methane is an extremely efficient
greenhouse gas which contributes to enhanced global warming. Other hydrocarbon VOCs are also significant greenhouse gases
because of their role in creating ozone and prolonging the life of methane in the atmosphere. This effect varies depending on local air quality. The aromatic
NMVOCs benzene, toluene and xylene are suspected carcinogens and
may lead to leukemia with prolonged exposure. 1,3-butadiene is
another dangerous compound often associated with industrial use.
- Particulates, alternatively referred to as particulate matter (PM), atmospheric
particulate matter, or fine particles, are tiny particles of solid
or liquid suspended in a gas. In contrast, aerosol refers to
combined particles and gas. Some particulates occur naturally,
originating from volcanoes, dust storms, forest and grassland
fires, living vegetation, and sea spray. Human activities, such as
the burning of fossil fuels in vehicles, power plants and various
industrial processes also generate significant amounts of aerosols.
Averaged worldwide, anthropogenic aerosols—those made by human
activities—currently account for approximately 10 percent of our
atmosphere. Increased levels of fine particles in the air are
linked to health hazards such as heart disease,[12][13] altered lung function and lung cancer.
- Persistent free radicals connected to airborne fine particles are linked to cardiopulmonary
disease.[14][15]
- Toxic metals, such as lead and mercury, especially their compounds.
- Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) - harmful to the ozone layer; emitted from products are currently banned from use. These are
gases which are released from air conditioners, refrigerators,
aerosol sprays, etc. On release into the air, CFCs rise to the stratosphere. Here they come in contact with other gases and damage the ozone layer. This allows harmful ultraviolet rays to reach the earth's
surface. This can lead to skin cancer, eye disease and can even
cause damage to plants.
- Ammonia (NH3) - emitted from agricultural processes. Ammonia is a compound with
the formula NH3. It is normally encountered as a gas with a characteristic pungent
odor. Ammonia contributes significantly to the nutritional needs of
terrestrial organisms by serving as a precursor to foodstuffs and
fertilizers. Ammonia, either directly or indirectly, is also a
building block for the synthesis of many pharmaceuticals. Although
in wide use, ammonia is both caustic and hazardous. In the
atmosphere, ammonia reacts with oxides of nitrogen and sulfur to
form secondary particles.[16]





