QINGDAO ENNENG MOTOR CO.,LTD. |
|
Verified Suppliers
|
|
High Reliability Multi Pole Rare Earth NdFeB PMAC Motor Price
What Is The Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor?
A PM motor is an ac motor that uses magnets embedded into or attached to the surface of the motor’s rotor. The magnets are used to generate a constant motor flux instead of requiring the stator field to generate one by linking to the rotor, as is the case with an induction motor.
Analysis of the principle of the technical advantages of permanent magnet motor
The principle of a permanent magnet synchronous motor is as follows: In the motor's stator winding into the three-phase current, after the pass-in current, it will form a rotating magnetic field for the motor's stator winding. Because the rotor is installed with the permanent magnet, the permanent magnet's magnetic pole is fixed, according to the principle of magnetic poles of the same phase attracting different repulsion, the rotating magnetic field generated in the stator will drive the rotor to rotate, the rotation speed of the rotor is equal to the speed of the rotating pole produced in the stator.
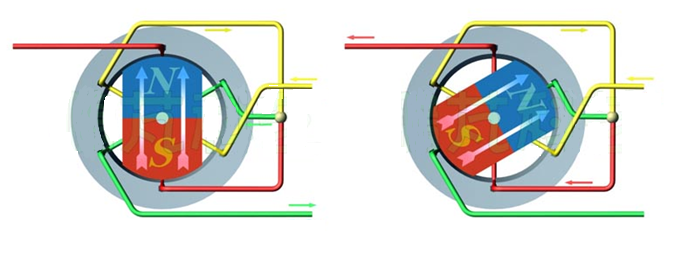
Due to the use of permanent magnets to provide magnetic fields, the rotor process is mature, reliable, and flexible in size, and the design capacity can be as small as tens of watts, up to megawatts. At the same time, by increasing or decreasing the number of pairs of rotor permanent magnets, it is easier to change the number of poles of the motor, which makes the speed range of permanent magnet synchronous motors wider. With multi-pole permanent magnet rotors, the rated speed can be as low as a single digit, which is difficult to achieve by ordinary asynchronous motors.
Especially in the low-speed high-power application environment, the permanent magnet synchronous motor can be directly driven by a multi-pole design at low speed, compared with an ordinary motor plus reducer, the advantages of a permanent magnet synchronous motor can be highlighted.


Permanent magnet AC (PMAC) motors have a wide range of applications including:
Industrial Machinery: PMAC motors are used in a variety of industrial machinery applications, such as pumps, compressors, fans, and machine tools. They offer high efficiency, high power density, and precise control, making them ideal for these applications.
Robotics: PMAC motors are used in robotics and automation applications, where they offer high torque density, precise control, and high efficiency. They are often used in robotic arms, grippers, and other motion control systems.
HVAC Systems: PMAC motors are used in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, where they offer high efficiency, precise control, and low noise levels. They are often used in fans and pumps in these systems.
Renewable Energy Systems: PMAC motors are used in renewable energy systems, such as wind turbines and solar trackers, where they offer high efficiency, high power density, and precise control. They are often used in the generators and tracking systems in these systems.
SPM versus IPM
A PM motor can be separated into two main categories: surface
permanent magnet motors (SPM) and interior permanent magnet motors
(IPM). Neither motor design type contains rotor bars. Both types
generate magnetic flux by the permanent magnets affixed to or
inside of the rotor.
SPM motors have magnets affixed to the exterior of the rotor surface. Because of this mechanical mounting, their mechanical strength is weaker than that of IPM motors. The weakened mechanical strength limits the motor’s maximum safe mechanical speed. In addition, these motors exhibit very limited magnetic saliency (Ld ≈ Lq). Inductance values measured at the rotor terminals are consistent regardless of the rotor position. Because of the near unity saliency ratio, SPM motor designs rely significantly, if not completely, on the magnetic torque component to produce torque.
IPM motors have a permanent magnet embedded into the rotor itself. Unlike their SPM counterparts, the location of the permanent magnets makes IPM motors very mechanically sound, and suitable for operating at very high speeds. These motors also are defined by their relatively high magnetic saliency ratio (Lq > Ld). Due to their magnetic saliency, an IPM motor has the ability to generate torque by taking advantage of both the magnetic and reluctance torque components of the motor.
PM motor structures
PM motor structures can be separated into two categories: interior
and surface. Each category has its subset of categories. A surface
PM motor can have its magnets on or inset into the surface of the
rotor, to increase the robustness of the design. An interior
permanent magnet motor positioning and design can vary widely. The
IPM motor’s magnets can be inset as a large block or staggered as
they come closer to the core. Another method is to have them
embedded in a spoke pattern.
PM motor inductance variation with load
Only so much flux can be linked to a piece of iron to generate
torque. Eventually, the iron will saturate and no longer allow flux
to link. The result is a reduction in the inductance of the path
taken by a flux field. In a PM machine, the d-axis and q-axis
inductance values will reduce with increases in the load current.
The d and q-axis inductances of an SPM motor are nearly identical. Because the magnet is outside of the rotor, the inductance of the q-axis will drop at the same rate as the d-axis inductance. However, the inductance of an IPM motor will reduce differently. Again, the d-axis inductance is naturally lower because the magnet is in the flux path and does not generate an inductive property. Therefore, there is less iron to saturate in the d-axis, which results in a significantly lower reduction in flux with respect to the q-axis.
PM motor magnet types
There are a few types of permanent magnet materials currently used for electric motors. Each type of metal has its advantages and disadvantages.
Main Features
Self-sensing versus closed-loop operation
Recent advances in drive technology allow standard ac drives to “self-detect” and track the motor magnet position. A closed-loop system typically uses the z-pulse channel to optimize performance. Through certain routines, the drive knows the exact position of the motor magnet by tracking the A/B channels and correcting for errors with the z-channel. Knowing the exact position of the magnet allows for optimum torque production resulting in optimum efficiency.
Flux weakening/intensifying of PM motors
Flux in a permanent magnet motor is generated by the magnets. The
flux field follows a certain path, which can be boosted or opposed.
Boosting or intensifying the flux field will allow the motor to
temporarily increase torque production. Opposing the flux field
will negate the existing magnet field of the motor. The reduced
magnet field will limit torque production, but reduce the back-emf
voltage. The reduced back-emf voltage frees up the voltage to push
the motor to operate at higher output speeds. Both types of
operation require additional motor current. The direction of the
motor current across the d-axis, provided by the motor controller, determines the desired effect.
Advantages Of Rare-earth Permanent Magnet Motors
High efficiency: The efficiency curve of the asynchronous motor generally falls faster under 60% of the rated load, and the efficiency is very low at light load. The efficiency curve of the rare earth permanent magnet motor is high and flat, and it is in the high-efficiency area at 20%~120% of the rated load.
High power factor: The measured value of the power factor of the rare earth permanent magnet synchronous motor is close to the limit value of 1.0. The power factor curve is as high and flat as the efficiency curve. The power factor is high. Low-voltage reactive power compensation is not required and the power distribution system capacity is fully utilized.
Stator current is small: The rotor has no excitation current, the reactive power is reduced, and the stator current is significantly reduced. Compared with the asynchronous motor of the same capacity, the stator current value can be reduced by 30% to 50%. At the same time, because the stator current is greatly reduced, the motor temperature rise is reduced, and the bearing grease and bearing life are extended.
High out-of-step torque and pull-in torque: Rare earth permanent magnet synchronous motors have higher out-of-step torque and pull-in torque, which makes the motor have higher load capacity and can be smoothly pulled into synchronization.
What applications use PMSM motors?
High-efficiency permanent magnet frequency conversion synchronous motors are widely used in injection molding machines, air compressors, pipe-making equipment, hydraulic machinery, food machinery, cement pipe-making machines, plastic extruders, wire drawing machines, and pharmaceutical equipment.